
His Finger Is Severely Infected Nail Biting Addiction Day in the Life Working Mom YouTube
ADHD stimming is when a person with ADHD displays self-stimulatory behavior by repeating certain sounds and movements unconsciously. There are many different examples, including lip biting, rocking back and forth, humming, teeth grinding, or chewing gum.. For instance, rather than chewing on your nails or biting the insides of your mouth.

Factors Influencing Nail Biting Habit in Children with ADHD International Journal of Child
"Nail Biting! Skin Picking! Hair Pulling! Understanding Body-Focused Repetitive Behaviors with ADHD" [Video Replay and Podcast #386] Access the video replay, listen to the podcast episode (#386), download the slide presentation, and learn how to get a certificate of attendance for this ADHD Experts webinar originally broadcast on January 26, 2022.

How to Stop Nailbiting One Trick to Stop Nail Biting · Pintsized Treasures
Nail biting (NB) is a common, but unresolved, problem in psychiatry, psychology, medicine and dentistry. While it seems that NB is a simple behavior that can be stopped easily, many of the children with NB have already tried to stop it, but they have not been successful.

Nail Biting Clarity Clinic
Touch (tactile): Nail biting, scratching, hair pulling or twirling, chewing the inside of the cheeks, teeth grinding, rubbing fingers Vestibular (balance-based): Rocking, spinning, shaking the head Can Eating Be a Sign of ADHD Stimming? Some people with ADHD may overeat as a way of stimulating the brain.
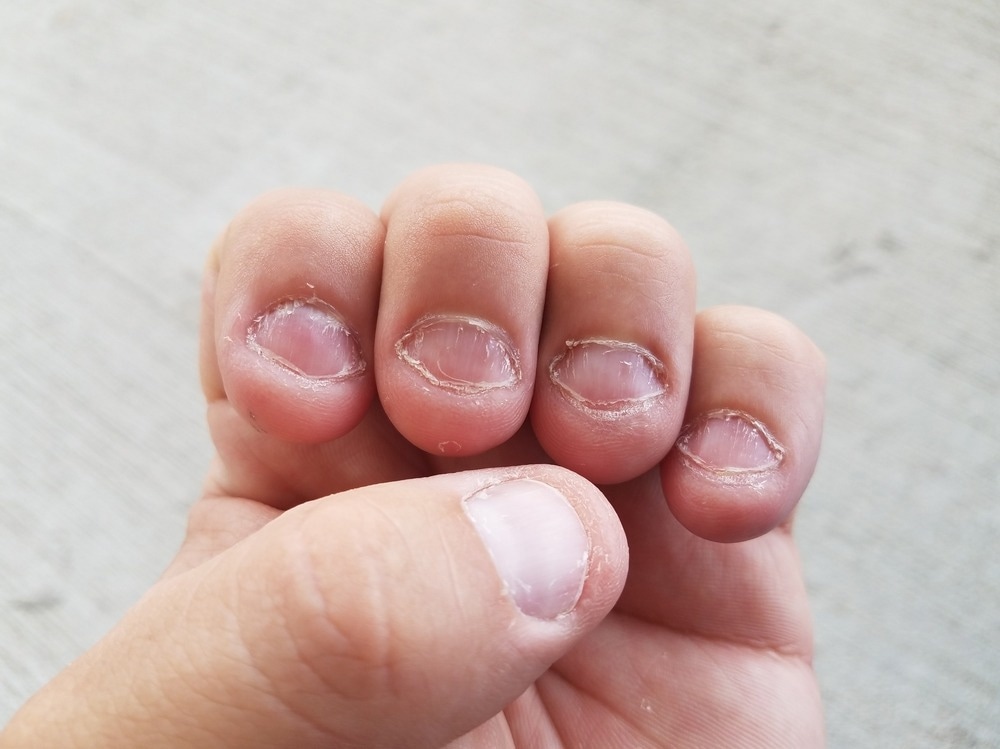

The Psychology Behind Nail Biting
Stimming, or self-stimulatory behavior, such as nail-biting, humming, or rocking, can be a very common human behavior and is often observed in people of all ages, backgrounds, and abilities.
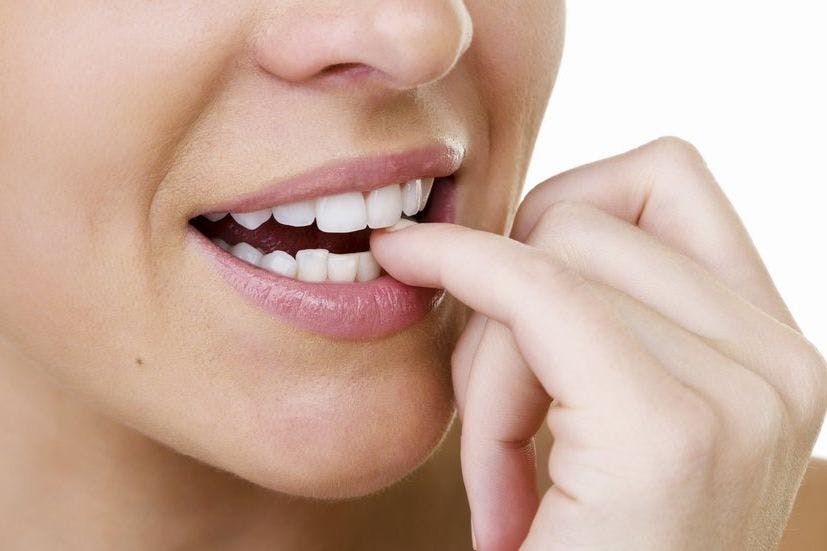

Scientists reveal surprising health benefits to biting your nails
Sep 17, 2021 — 5 min read Article tags: Personal narrative Sensory processing Dopamine Table of contents: Body-focused repetitive behaviors (BFRBs) The link between ADHD and body-focused repetitive behaviors The vicious cycle of ADHD and hair-pulling or nail-biting Why are ADHDers prone to body-focused repetitive behaviors?
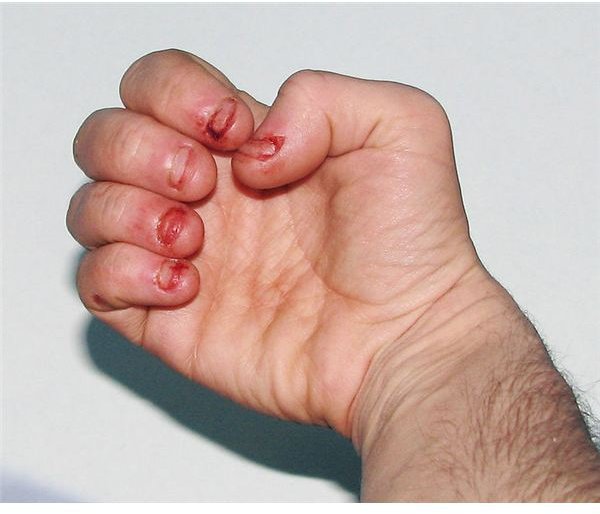
Onychophagia How to Nail Biting OCD
Body-focused repetitive behaviors (BFRBs) refer to recurrent and chronic behaviors inflicted upon the body (like nail biting and hair pulling) that often result in physical damage. Examples of BFRBs include: Trichotillomania (hair-pulling disorder) Excoriation/Dermatillomania (skin-picking disorder) Onychophagia (nail biting)

After Reading The Hazards And Adverse Effects Of Nail Biting You Will Never Bite Your Nails Again
How do people stop biting their nails? When you're a chronic nail biter, you often want to stop — and may have even made multiple attempts to quit, without success. Bur people with onychophagia can't stop the behavior on their own.
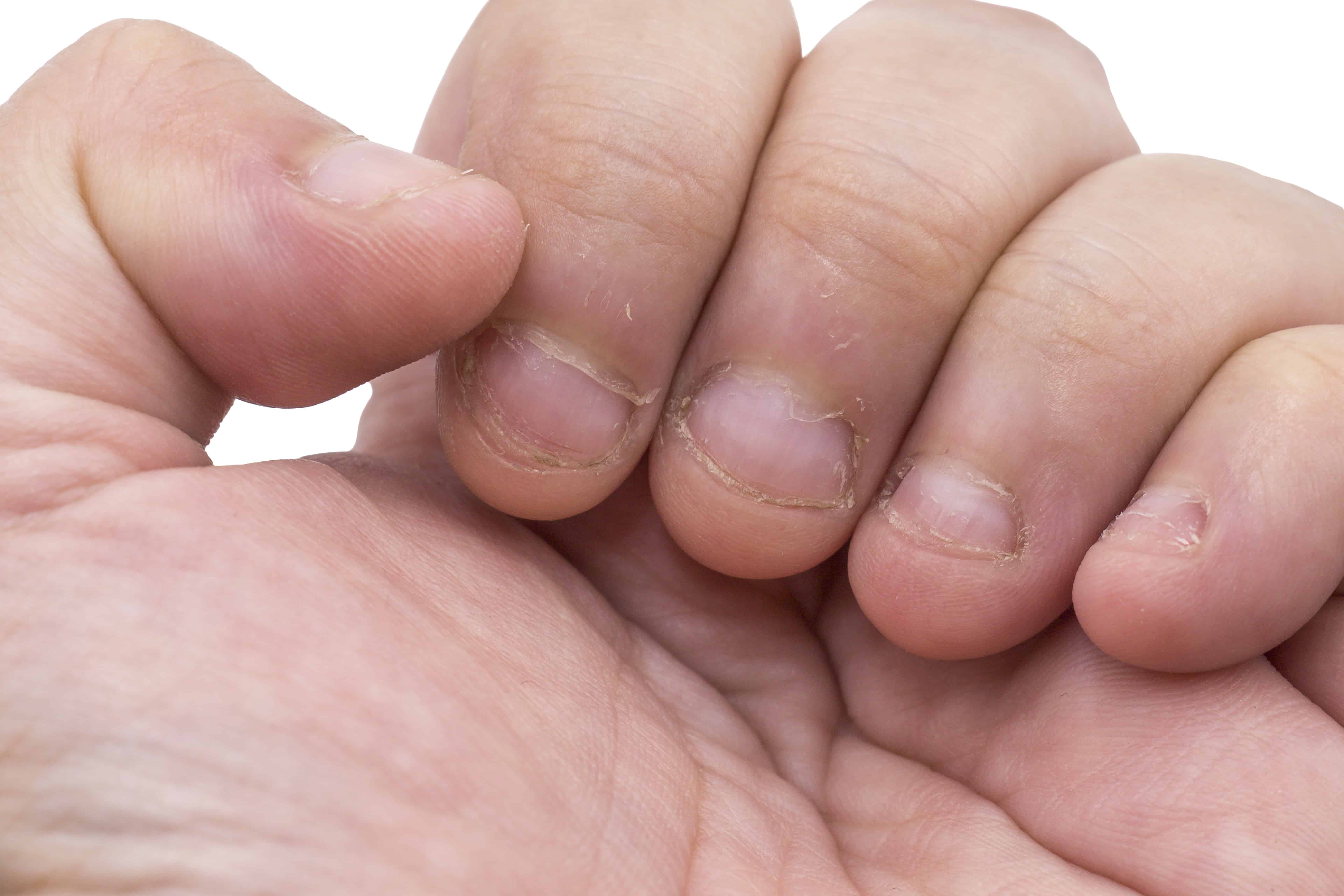

Nail Biting Dermatologist Cape Town Dr Matete Mathobela
The Answer to Incessant Nail and Skin Biting? Fidget Rings It took me 57 years to get an ADHD diagnosis. It took 57 years and three weeks for my BFRB to take a turn for the better. I have fidget rings to thank for that. I had been reading about and experimenting with fidget toys for ADHD when I discovered the existence of fidget rings.
/GettyImages-462539777-5a402842b39d03003721104c.jpg)
Strategies To Stop Kids From Biting Their Nails Radio Sargam
Body-focused repetitive behaviors, or BFRBs, are a set of disorders categorized by self-grooming routines that essentially go awry. These include pulling, picking, biting, or scraping one's.

Nail biting habit in children and adult, causes and nail biting treatment
BFRBs comprise a variety of behaviors, including skin picking; skin biting; hair pulling; nail biting; nose picking, and similar activities involving the inside of the mouth, cheek, inner lip or tongue. The conditions range from mild to severe and play out differently depending on the child.

How Nail Biting Could Prove Harmful and Dangerous to Your Health Top 10 Home Remedies
Almost everyone stims: think hair twirling or nail-biting. For folks with conditions such as autism or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), stimming may be harder to control,.
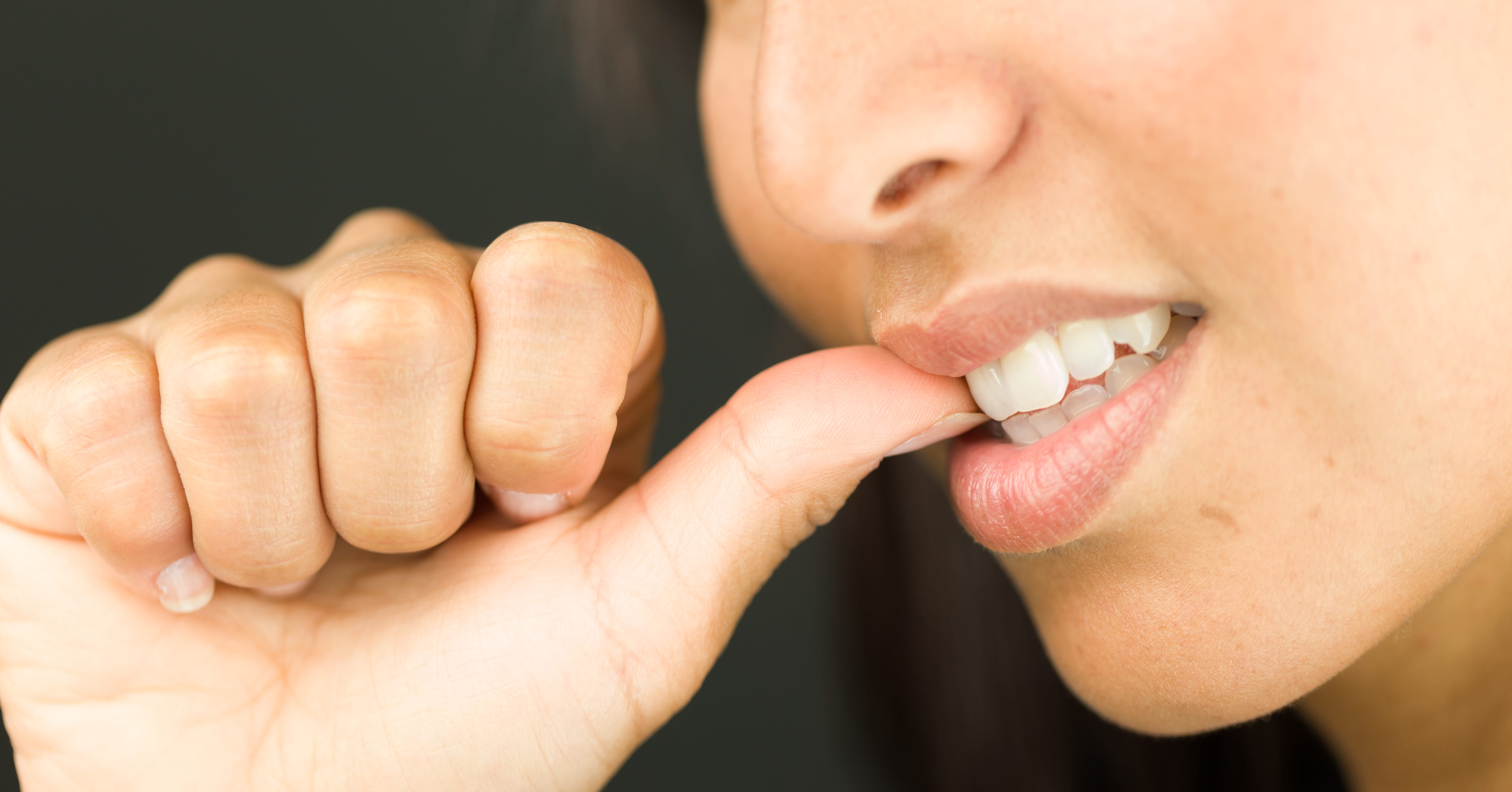

Is Biting Your Nails Actually Dangerous? Banner Health
Prevalence and etiology. The current literature estimates the prevalence of nail biting at 20% to 30% of the general population (Halteh et al., 2017, Pacan et al., 2014).Nail biting is more prevalent in children, with one study noting a 37% prevalence among individuals age 3 to 21 years (Winebrake et al., 2018) Fig. 1.Leung and Robson (1990) describe a downward trend in prevalence as affected.

PPT NAIL BITING PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1851297
Scientific Definition. ADHD nail biting is known as "onychophagia.". It's a behavior often observed in children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder ( ADHD ). Onychophagia is the repetitive and sometimes compulsive act of biting or chewing one's nails. This habit can be triggered by anxiety, restlessness, or inattention, which.
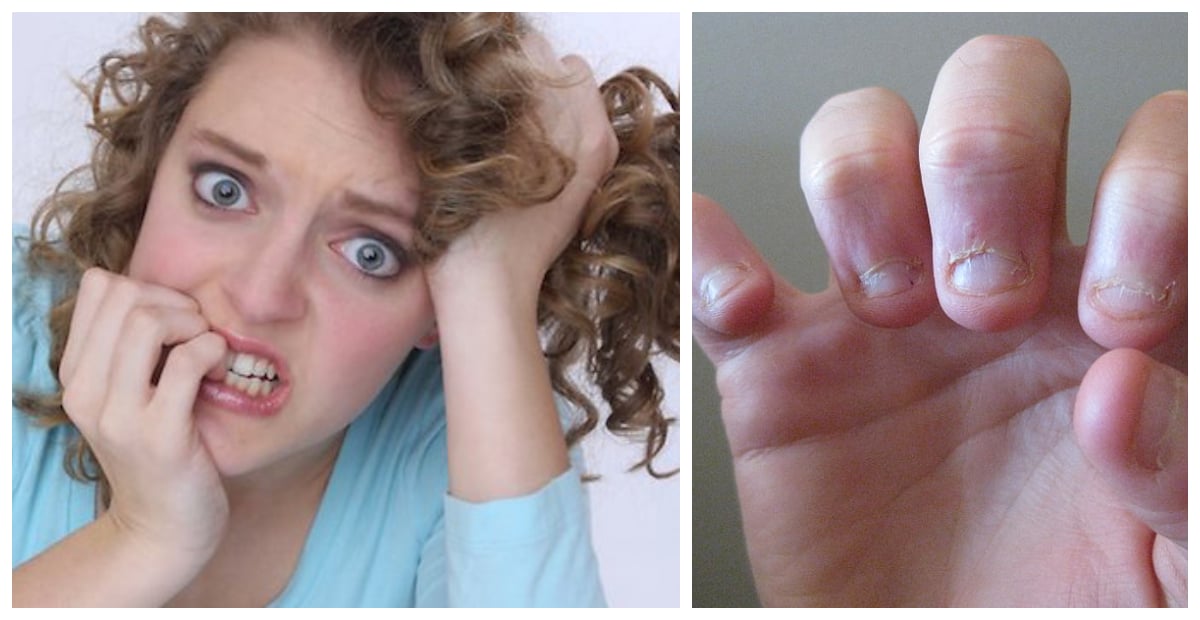
Research Finally Reveals The Real Reason We Bite Our Nails
feelings of shame, embarrassment, anxiety, or guilt, often related to the appearance of physical damage to skin and nails caused by biting fear of others seeing one's nails or being disgusted.
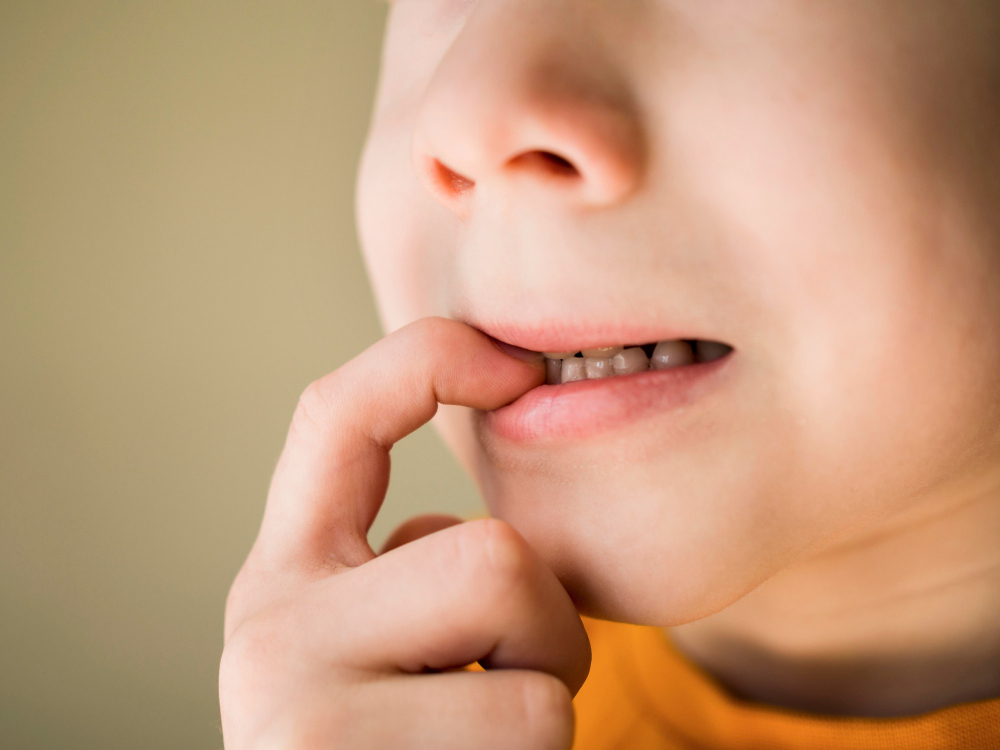

ADHD u dzieci i dorosłych eDoktorzy ERecepta EZwolnienie
Introduction: Nail biting is a common habit that affects people of all ages, often serving as a response to stress, anxiety, or nervousness. While it is generally considered a harmless behavior, recent research has shed light on a potential link between nail biting and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).